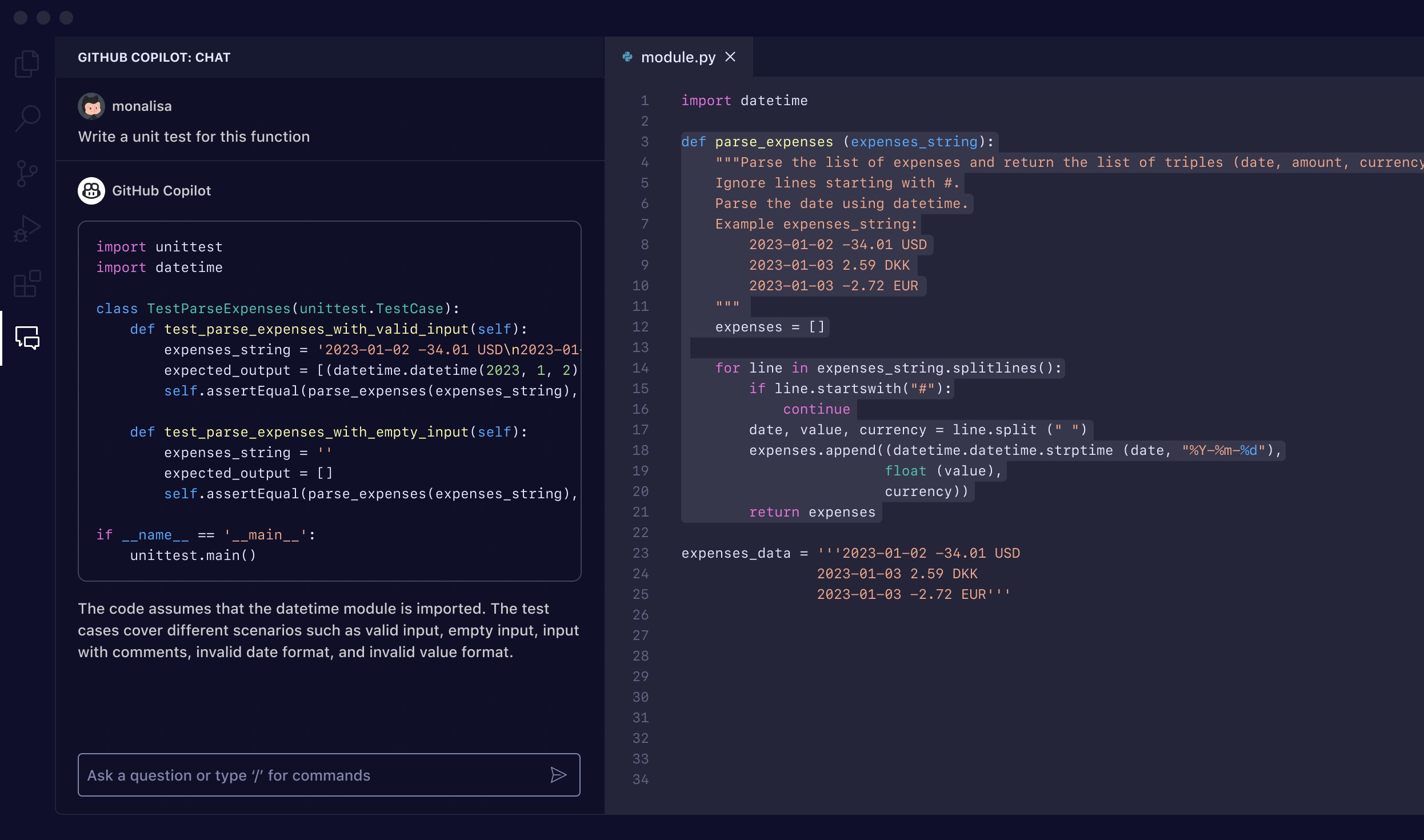
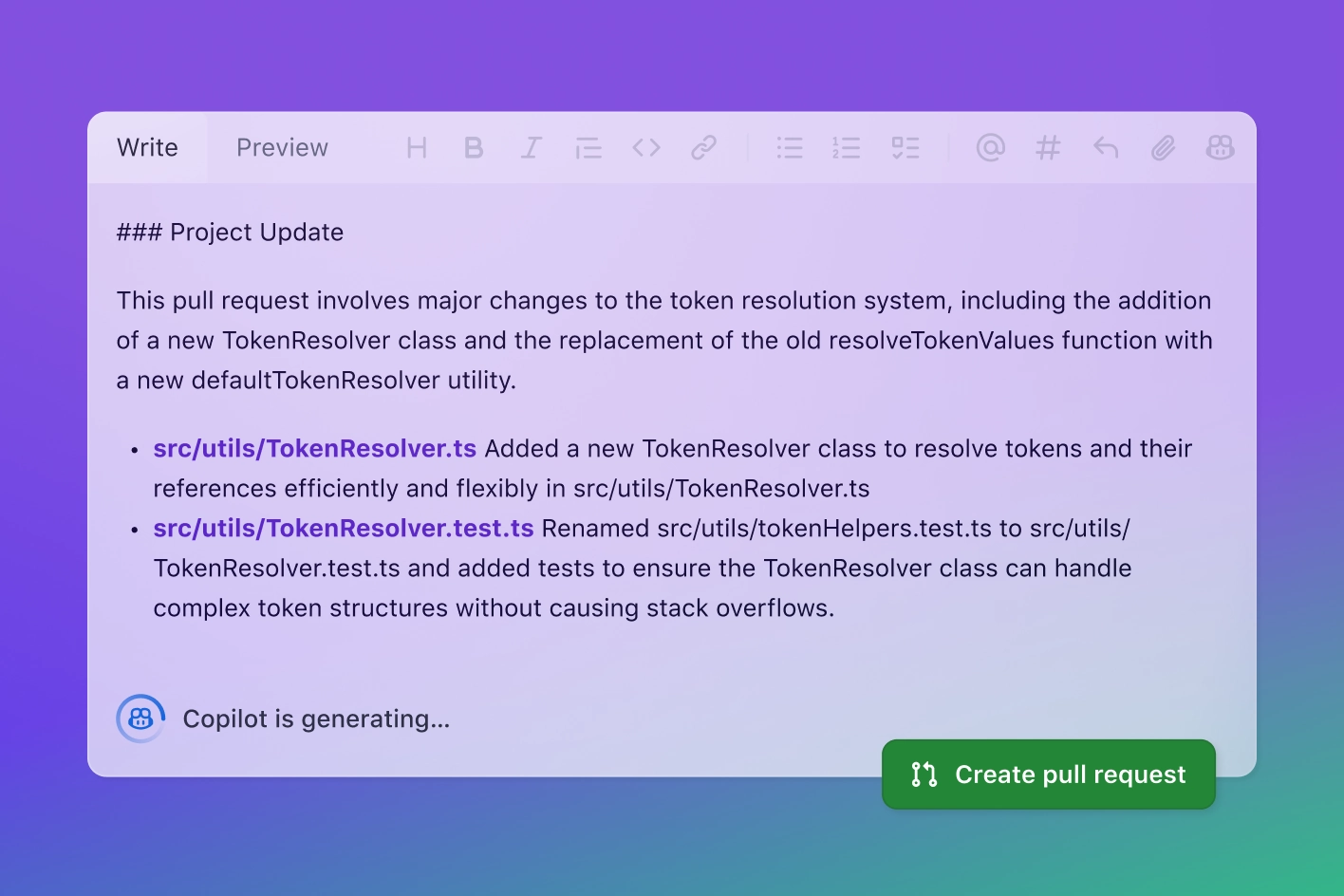
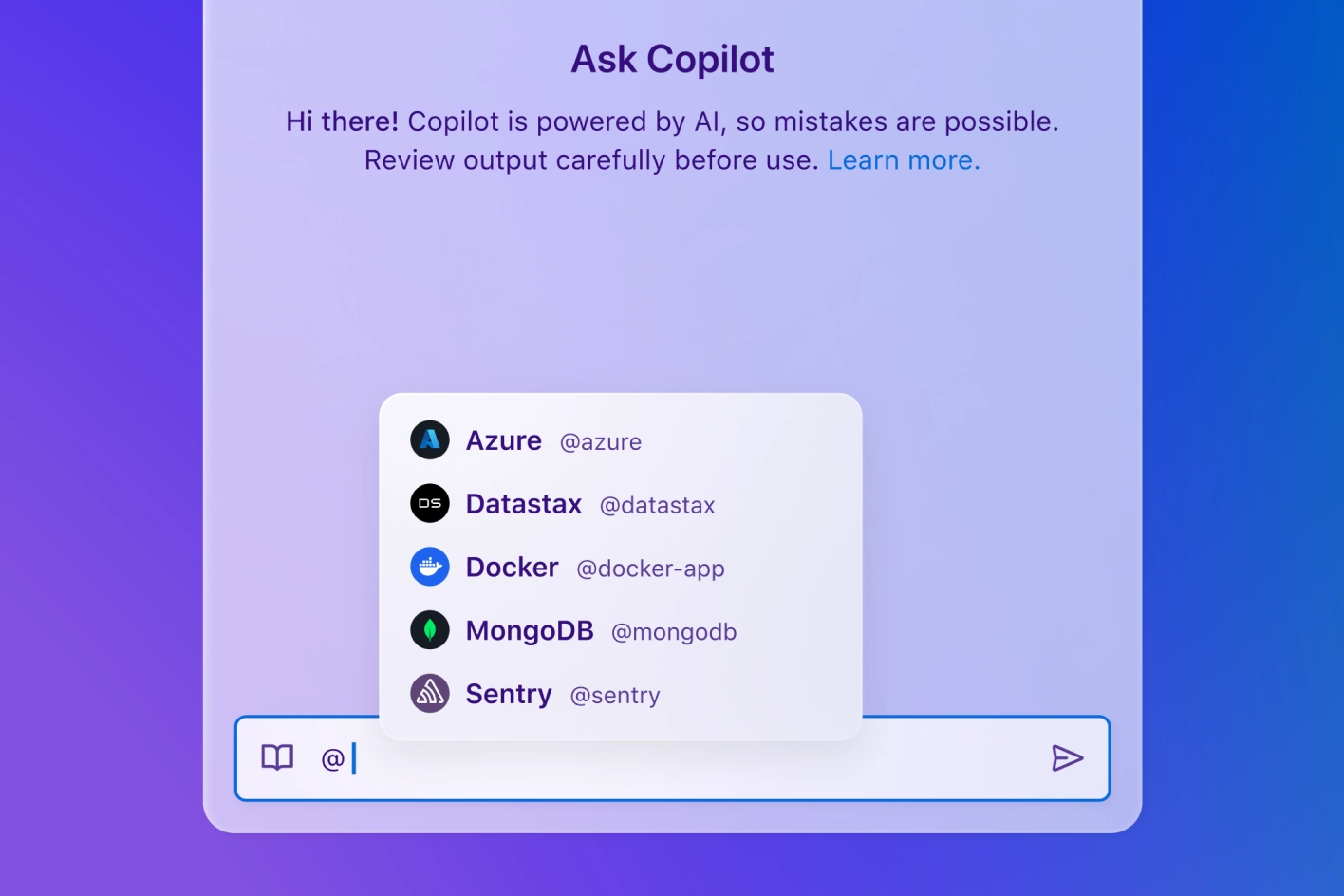
Start a conversation about your codebase. Whether you’re hunting down a bug or designing a new feature—when you’re stuck, ask
GitHub Copilot.
The world’s most widely adopted AI developer tool.
GitHub Copilot is used by
The competitive advantage developers ask for by name.
Proven to increase developer productivity and accelerate the pace of software development.
Read the research
55%
Faster coding

Designed by leaders in AI so you can build with confidence.

Committed to your privacy, security, and trust.
Visit the GitHub Copilot Trust Center
Duolingo empowers its engineers to be force multipliers for expertise with GitHub Copilot, Codespaces.
Read customer story~25%
increase in developer speed with GitHub Copilot
1m
set-up time for largest repo with Codespaces
Problem
Inconsistent standards and workflows limited developer mobility and efficiency, limiting Duolingo’s ability to expand its content and deliver on its core mission.
Solution
GitHub Copilot, Codespaces, and custom API integrations enforce code consistency, accelerate developer speed, and remove the barriers to using engineering as a force multiplier for expertise.
The industry
standard.

The AI coding assistant
elevating developer workflows.
- Improve code quality and security. Developers feel more confident in their code quality when authoring code with GitHub Copilot. And with the built-in vulnerability prevention system, insecure coding patterns get blocked in real time.
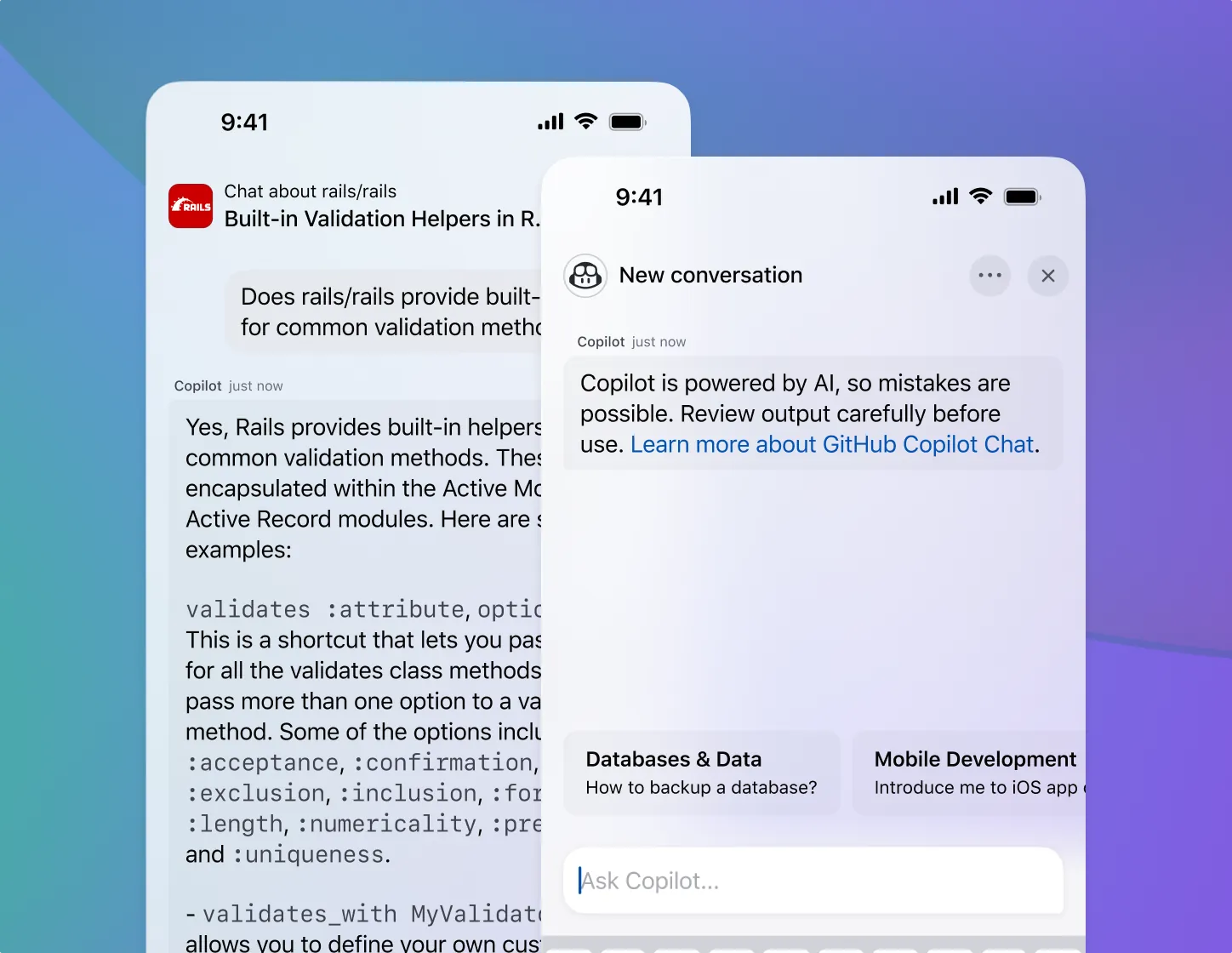
- Enable greater collaboration. GitHub Copilot’s the newest member of your team. You can ask general programming questions or very specific ones about your codebase to get answers fast, learn your way around, explain a mysterious regex, or get suggestions on how to improve legacy code.
Get AI-based suggestions in real time.
GitHub Copilot suggests code completions as developers type and turns natural language prompts into coding suggestions based on the project's context and style conventions.
Available for Copilot EnterpriseDocs that feel tailored for you.
Spend less time searching and more time learning, by getting personalized answers that are grounded in your organization’s knowledge base, with inline citations. Load content → Ask question → Profit.
Available for Copilot EnterprisePull requests that tell a story.
GitHub Copilot keeps track of your work, suggests descriptions, and helps reviewers reason about your changes.
Limited BetaYour favorite tools have entered the chat.
Check log errors, create feature flags, deploy apps to the cloud. Add capabilities to GitHub Copilot with an ecosystem of extensions from third-party tools and services.
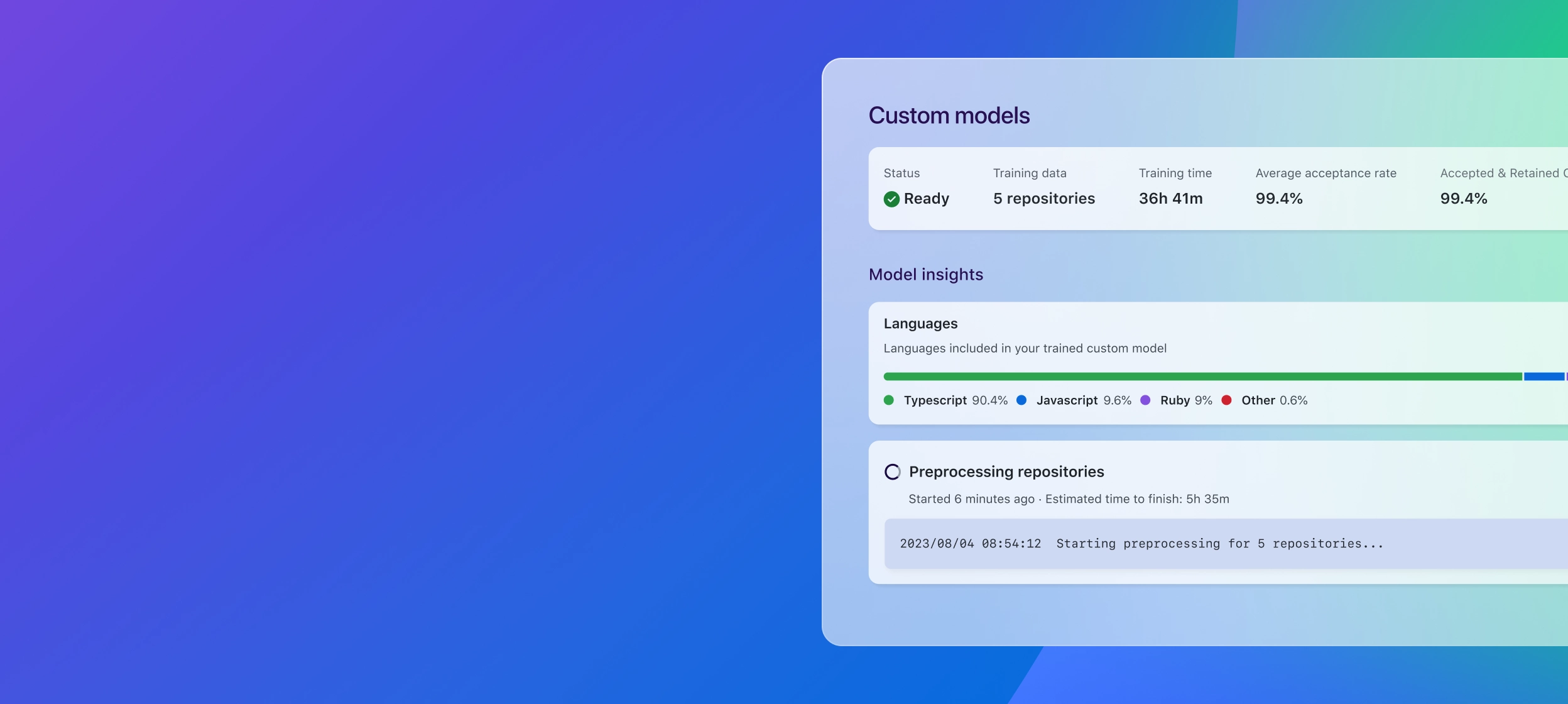
Coming soon as an add-onPrefer bespoke? Fine-tune a private, custom model that suggests code based on the best practices and patterns in your repositories.
Ask for assistance right in your terminal.
Try Copilot in the CLI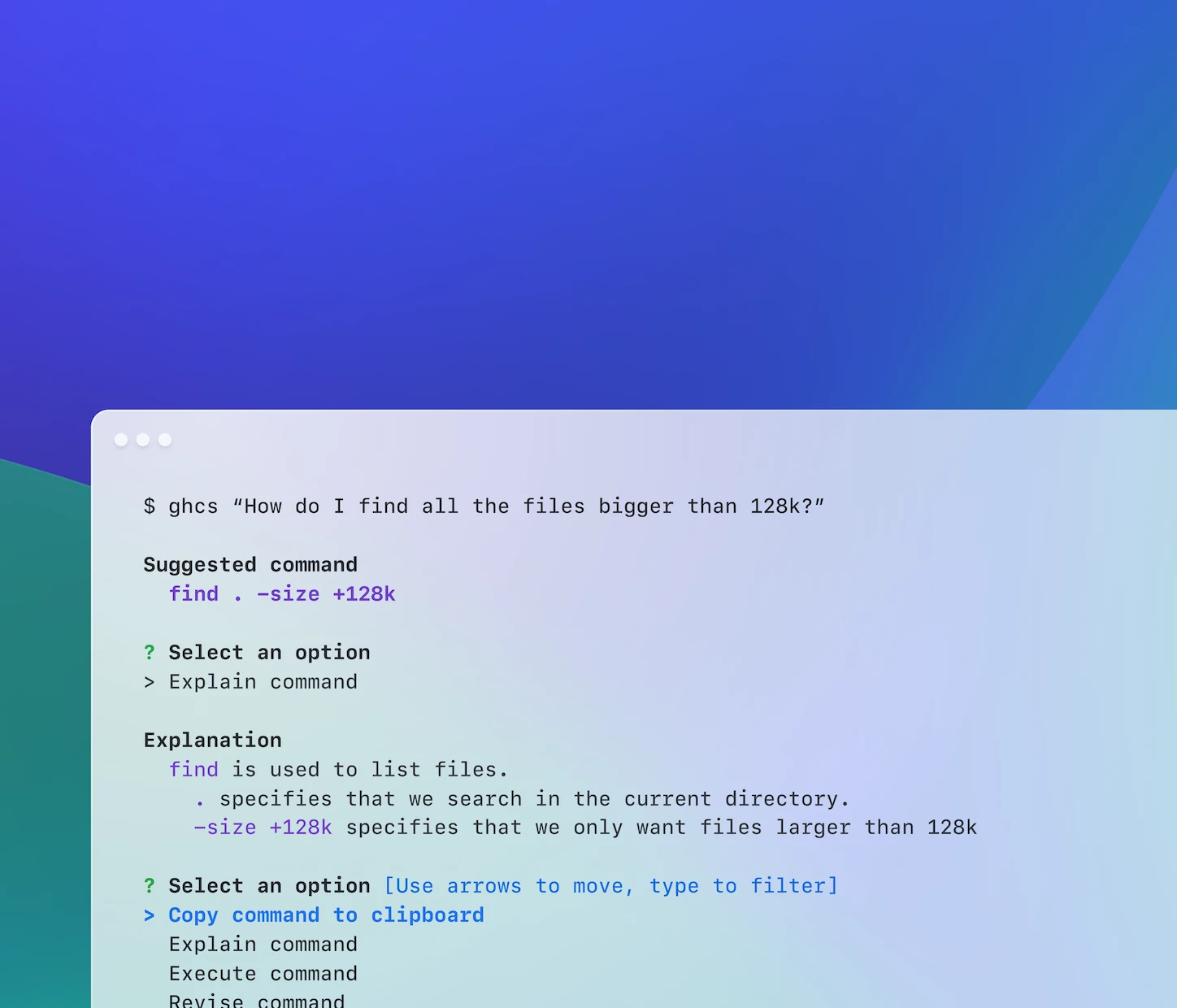
Keep flying with your favorite editor.

Take flight with GitHub Copilot.
Organizations and developers all over the world use GitHub Copilot to code faster, drive impact, and focus on doing what matters most: building great software.
Copilot
Individual
For individual developers, freelancers, students, and educators that want to code faster and happier.
Copilot
Business
For organizations ready to improve engineering velocity, code quality, and developer experience.
Copilot
Enterprise
For companies looking to customize GitHub Copilot to their organization and infuse AI across the developer workflow.

Individual
Business
Enterprise
Get the most out of GitHub Copilot.
Frequently asked questions.
General
What is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot transforms the developer experience. Backed by the leaders in AI, Copilot provides contextualized assistance throughout the software development lifecycle, from code completions and chat assistance in the IDE to code explanations and answers to docs in GitHub and more. With Copilot elevating their workflow, developers can focus on more: value, innovation, and happiness.
GitHub Copilot enables developers to focus more energy on problem solving and collaboration and spend less effort on the mundane and boilerplate. That’s why developers who use Copilot report up to 75% higher satisfaction with their jobs than those who don’t and are up to 55% more productive at writing code without sacrifice to quality, which all adds up to engaged developers shipping great software faster. without sacrifice to quality, which all adds up to engaged developers shipping great software faster.
GitHub Copilot integrates with leading editors, including Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, and Neovim, and, unlike other AI coding assistants, is natively built into GitHub. Growing to millions of individual users and tens of thousands of business customers, Copilot is the world’s most widely adopted AI developer tool and the competitive advantage developers ask for by name.
What are the differences between the GitHub Copilot Business, GitHub Copilot Enterprise, and GitHub Copilot Individual plans?
GitHub Copilot has multiple offerings for organizations and an offering for individual developers. All the offerings include both code completion and chat assistance. The primary differences between the organization offerings and the individual offering are license management, policy management, and IP indemnity.
Organizations can choose between GitHub Copilot Business and GitHub Copilot Enterprise. GitHub Copilot Business primarily features GitHub Copilot in the coding environment - that is the IDE, CLI and GitHub Mobile. GitHub Copilot Enterprise includes everything in GitHub Copilot Business. It also adds an additional layer of customization for organizations and integrates into GitHub.com as a chat interface to allow developers to converse with Copilot throughout the platform. GitHub Copilot Enterprise can index an organization’s codebase for a deeper understanding of the customer’s knowledge for more tailored suggestions and will offer customers access to fine-tuned custom, private models for code completion.
GitHub Copilot Individual is designed for individual developers, freelancers, students, educators, and open source maintainers. The plan includes all the features of GitHub Copilot Business except organizational license management, policy management, and IP indemnity.
What languages, IDEs, and platforms does GitHub Copilot support?
GitHub Copilot is trained on all languages that appear in public repositories. For each language, the quality of suggestions you receive may depend on the volume and diversity of training data for that language. For example, JavaScript is well-represented in public repositories and is one of GitHub Copilot’s best supported languages. Languages with less representation in public repositories may produce fewer or less robust suggestions.
GitHub Copilot is available as an extension in Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, Vim, Neovim, the JetBrains suite of IDEs, and Azure Data Studio. Although code completion functionality is available across all these extensions, chat functionality is currently available only in Visual Studio Code, JetBrains and Visual Studio. GitHub Copilot is also supported in terminals through GitHub CLI. With the GitHub Copilot Enterprise plan, GitHub Copilot is natively integrated into GitHub.com. All plans are supported in GitHub Copilot in GitHub Mobile. GitHub Mobile for Copilot Individual and Copilot Business have access to Bing and public repository code search. Copilot Enterprise in GitHub Mobile gives you additional access to your organization's knowledge.
What data has GitHub Copilot been trained on?
GitHub Copilot is powered by generative AI models developed by GitHub, OpenAI, and Microsoft. It has been trained on natural language text and source code from publicly available sources, including code in public repositories on GitHub.
Does GitHub Copilot “copy/paste”?
No, GitHub Copilot generates suggestions using probabilistic determination.
When thinking about intellectual property and open source issues, it is critical to understand how GitHub Copilot really works. The AI models that create Copilot’s suggestions may be trained on public code, but do not contain any code. When they generate a suggestion, they are not “copying and pasting” from any codebase.
To generate a code suggestion, the Copilot extension begins by examining the code in your editor—focusing on the lines just before and after your cursor, but also information including other files open in your editor and the URLs of repositories or file paths to identify relevant context. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
To generate a suggestion for chat in the code editor, the Copilot extension creates a contextual prompt by combining your prompt with additional context including the code file open in your active document, your code selection, and general workspace information, such as frameworks, languages, and dependencies. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
To generate a suggestion for chat on GitHub.com, such as providing an answer to a question from your chat prompt, Copilot creates a contextual prompt by combining your prompt with additional context including previous prompts, the open pages on GitHub.com as well as retrieved context from your codebase or Bing search. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
Privacy
What personal data does GitHub Copilot process?
GitHub Copilot processes personal data based on how Copilot is accessed and used: whether via GitHub.com, mobile app, extensions, or one of various IDE extensions, or through features like suggestions for the command line interface (CLI), IDE code completions, or personalized chat on GitHub.com. The types of personal data processed may include:
User Engagement Data: This includes pseudonymous identifiers captured on user interactions with Copilot, such as accepted or dismissed completions, error messages, system logs, and product usage metrics.
Prompts: These are inputs for chat or code, along with context, sent to Copilot's AI to generate suggestions.
Suggestions: These are the AI-generated code lines or chat responses provided to users based on their prompts.
Feedback Data: This comprises real-time user feedback, including reactions (e.g., thumbs up/down) and optional comments, along with feedback from support tickets.
Does GitHub use Copilot Business or Enterprise data to train GitHub’s model?
No. GitHub does not use either Copilot Business or Enterprise data to train its models.
How does GitHub use the Copilot data?
How GitHub uses Copilot data depends on how the user accesses Copilot and for what purpose. Users can access GitHub Copilot through the web, extensions, mobile apps, computer terminal, and various IDEs (Integrated Development Environments). GitHub generally uses personal data to:
Deliver, maintain, and update the services as per the customer's configuration and usage, to ensure personalized experiences and recommendations
Troubleshoot, which involves preventing, detecting, resolving, and mitigating issues, including security incidents and product-related problems, by fixing software bugs and maintaining the online services' functionality and up-to-dateness
Enhance user productivity, reliability, effectiveness, quality, privacy, accessibility, and security by keeping the service current and operational
These practices are outlined in GitHub’s Data Protection Agreement (DPA), which details our data handling commitments to our data controller customers.
GitHub also uses certain personal data with customer authorization under the DPA, for the following purposes:
Billing and account management
To comply with and resolve legal obligations
For abuse detection, prevention, and protection, virus scanning, and scanning to detect violations of terms of service
To generate summary reports for calculating employee commissions and partner incentives
To produce aggregated reports for internal use and strategic planning, covering areas like forecasting, revenue analysis, capacity planning, and product strategy,
For details on GitHub's data processing activities as a controller, particularly for Copilot Individual customers, refer to the GitHub Privacy Statement.
How long does GitHub retain Copilot data for Business and Enterprise customers?
If and for how long GitHub’s retains Copilot data depends on how a Copilot user accesses Copilot and for what purpose. The default settings for Copilot Business and Enterprise Customers are as follows:
Access through IDE for Chat and Code Completions:
Prompts and Suggestions: Not retained
User Engagement Data: Kept for two years.
Feedback Data: Stored for as long as needed for its intended purpose.
All other GitHub Copilot access and use:
Prompts and Suggestions: Retained for 28 days.
User Engagement Data: Kept for two years.
Feedback Data: Stored for as long as needed for its intended purpose.
Why do some Copilot features retain prompts and suggestions?
Retaining prompts and suggestions is necessary for chat on github.com, mobile, and CLI Copilot because those features’ effectiveness depends on using thread history to improve responses. The Copilot model requires access to previous interactions to deliver accurate and relevant suggestions.
Does GitHub Copilot support compliance with the GDPR and other data protection laws?
Yes. GitHub and customers can enter a Data Protection Agreement that supports compliance with the GDPR and similar legislation.
Does GitHub Copilot ever output personal data?
While we've designed GitHub Copilot with privacy in mind, the expansive definition of personal data under legislation like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) means we can't guarantee it will never output such data. The Large Language Model (LLM) powering GitHub Copilot was trained on public code and there were instances in our tests where the tool made suggestions resembling personal data. These suggestions were typically synthesized and not tied to real individuals.
How does Copilot allow users to access, alter or delete personal data?
These actions are available to Copilot users as described in the GitHub Privacy Statement.
Responsible AI
What are the intellectual property considerations when using GitHub Copilot?
The primary IP considerations for GitHub Copilot relate to copyright. The model that powers Copilot is trained on a broad collection of publicly accessible code, which may include copyrighted code, and Copilot’s suggestions (in rare instances) may resemble the code its model was trained on. Here’s some basic information you should know about these considerations:
Copyright law permits the use of copyrighted works to train AI models: Countries around the world have provisions in their copyright laws that enable machines to learn, understand, extract patterns, and facts from copyrighted materials, including software code. For example, the European Union, Japan, and Singapore, have express provisions permitting machine learning to develop AI models. Other countries including Canada, India, and the United States also permit such training under their fair use/fair dealing provisions. GitHub Copilot’s AI model was trained with the use of code from GitHub’s public repositories—which are publicly accessible and within the scope of permissible copyright use.
What about copyright risk in suggestions? In rare instances (less than 1% based on GitHub’s research), suggestions from GitHub may match examples of code used to train GitHub’s AI model. Again, Copilot does not “look up” or “copy and paste” code, but is instead using context from a user’s workspace to synthesize and generate a suggestion.
Our experience shows that matching suggestions are most likely to occur in two situations: (i) when there is little or no context in the code editor for Copilot’s model to synthesize, or (ii) when a matching suggestion represents a common approach or method. If a code suggestion matches existing code, there is risk that using that suggestion could trigger claims of copyright infringement, which would depend on the amount and nature of code used, and the context of how the code is used. In many ways, this is the same risk that arises when using any code that a developer does not originate, such as copying code from an online source, or reusing code from a library. That is why responsible organizations and developers recommend that users employ code scanning policies to identify and evaluate potential matching code.
In Copilot, you can opt whether to allow Copilot to suggest code completions that match publicly available code on GitHub.com. For more information, see "Configuring GitHub Copilot settings on GitHub.com". If you have allowed suggestions that match public code, GitHub Copilot can provide you with details about the matching code when you accept such suggestions. Matching code does not necessarily mean copyright infringement, so it is ultimately up to the user to determine whether to use the suggestion, and what and who to attribute (along with other license compliance) in appropriate circumstances.
Does GitHub Copilot include a filtering mechanism to mitigate risk?
Yes, GitHub Copilot does include an optional code referencing filter to detect and suppress certain suggestions that match public code on GitHub.
GitHub has created a duplication detection filter to detect and suppress suggestions that contain code segments over a certain length that match public code on GitHub. This filter can be enabled by the administrator for your enterprise and it can apply for all organizations within your enterprise, or the administrator can defer control to individual organizations.
With the filter enabled, Copilot checks code suggestions for matches or near-matches against public code on GitHub of 65 lexemes or more (on average,150 characters). If there is a match, the suggestion will not be shown to the user.
In addition to off-topic, harmful, and offensive output filters, GitHub Copilot also scans the outputs for vulnerable code.
Does GitHub Copilot include features to make it easier for users to identify potentially relevant open source licenses for matching suggestions?
Yes, GitHub Copilot is previewing a code referencing feature as an additional tool to assist users to find and review potentially relevant open source licenses. Code referencing is currently available in Visual Studio Code. This feature searches across public GitHub repositories for code that matches a Copilot suggestion. If there’s a match, users will find its information displayed in the Copilot console log, including where the match occurred, any applicable licenses, and a deep link to learn more. The deep link will take users to a navigable page on GitHub.com to browse examples of the code match and their repository licenses, and see how many repositories—including ones without licenses—that code appears in, as well as links to those repositories. Copilot users can review this information to determine whether the applicable suggestions are suitable for use, and whether additional measures may be necessary to use them.
Who owns the suggestions provided by GitHub Copilot?
We don’t determine whether a suggestion is capable of being owned, but we are clear that GitHub does not claim ownership of a suggestion. Whether a suggestion generated by an AI model can be owned depends on many factors (e.g. the intellectual property law in the relevant country, the length of the suggestion, the extent that suggestion is considered ‘functional’ instead of expressive, etc).
If a suggestion is capable of being owned, our terms are clear: GitHub does not claim ownership.
GitHub does not claim ownership of any suggestion. In certain cases, it is possible for Copilot to produce similar suggestions to different users. For example, two unrelated users both starting new files to code the quicksort algorithm in Java will likely get the same suggestion. The possibility of providing similar suggestions to multiple users is a common part of generative AI systems.
Can GitHub Copilot introduce insecure code in its suggestions?
Public code may contain insecure coding patterns, bugs, or references to outdated APIs or idioms. When GitHub Copilot synthesizes code suggestions based on this data, it can also synthesize code that contains these undesirable patterns. Copilot has filters in place that either block or notify users of insecure code patterns that are detected in Copilot suggestions. These filters target the most common vulnerable coding patterns, including hardcoded credentials, SQL injections, and path injections. Additionally, in recent years we’ve provided tools such as GitHub Advanced Security, GitHub Actions, Dependabot, and CodeQL to open source projects to help improve code quality. Of course, you should always use GitHub Copilot together with good testing and code review practices and security tools, as well as your own judgment.
Is GitHub Copilot intended to fully automate code generation and replace developers?
No. Copilot is a tool intended to make developers more efficient. It’s not intended to replace developers, who should continue to apply the same sorts of safeguards and diligence they would apply with regard to any third-party code of unknown origin.
The product is called “Copilot” not “Autopilot” and it’s not intended to generate code without oversight. You should use exactly the same sorts of safeguards and diligence with Copilot’s suggestions as you would use with any third-party code.
Identifying best practices for use of third party code is beyond the scope of this section. That said, whatever practices your organization currently uses – rigorous functionality testing, code scanning, security testing, etc. – you should continue these policies with Copilot’s suggestions. Moreover, you should make sure your code editor or editor does not automatically compile or run generated code before you review it.
Can GitHub Copilot users simply use suggestions without concern?
Not necessarily. GitHub Copilot users should align their use of Copilot with their respective risk tolerances.
As noted above, GitHub Copilot is not intended to replace developers, or their individual skill and judgment, and is not intended to fully automate the process of code development. The same risks that apply to the use of any third-party code apply to the use of Copilot’s suggestions.
Depending on your particular use case, you should consider implementing the protections discussed above. It is your responsibility to assess what is appropriate for the situation and implement appropriate safeguards.
You’re entitled to IP indemnification from GitHub for the unmodified suggestions when Copilot’s filtering is enabled. If you do elect to enable this feature, the copyright responsibility is ours, not our customers. As part of our ongoing commitment to responsible AI, GitHub and Microsoft extends our IP indemnity and protection support to our customers who are empowering their teams with GitHub Copilot. See Microsoft's Copilot Copyright Commitment for more details.
Does GitHub Copilot support accessibility features?
We are conducting internal testing of GitHub Copilot’s ease of use by developers with disabilities and working to ensure that GitHub Copilot is accessible to all developers. Please feel free to share your feedback on GitHub Copilot accessibility in our feedback forum.
Does GitHub Copilot produce offensive outputs?
GitHub Copilot includes filters to block offensive language in the prompts and to avoid synthesizing suggestions in sensitive contexts. We continue to work on improving the filter system to more intelligently detect and remove offensive outputs. If you see offensive outputs, please report them directly to copilot-safety@github.com so that we can improve our safeguards. GitHub takes this challenge very seriously and we are committed to addressing it.
Will GitHub Copilot work as well using languages other than English?
Given public sources are predominantly in English, GitHub Copilot will likely work less well in scenarios where natural language prompts provided by the developer are not in English and/or are grammatically incorrect. Therefore, non-English speakers might experience a lower quality of service.
General
What is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot transforms the developer experience. Backed by the leaders in AI, Copilot provides contextualized assistance throughout the software development lifecycle, from code completions and chat assistance in the IDE to code explanations and answers to docs in GitHub and more. With Copilot elevating their workflow, developers can focus on more: value, innovation, and happiness.
GitHub Copilot enables developers to focus more energy on problem solving and collaboration and spend less effort on the mundane and boilerplate. That’s why developers who use Copilot report up to 75% higher satisfaction with their jobs than those who don’t and are up to 55% more productive at writing code without sacrifice to quality, which all adds up to engaged developers shipping great software faster. without sacrifice to quality, which all adds up to engaged developers shipping great software faster.
GitHub Copilot integrates with leading editors, including Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, and Neovim, and, unlike other AI coding assistants, is natively built into GitHub. Growing to millions of individual users and tens of thousands of business customers, Copilot is the world’s most widely adopted AI developer tool and the competitive advantage developers ask for by name.
What are the differences between the GitHub Copilot Business, GitHub Copilot Enterprise, and GitHub Copilot Individual plans?
GitHub Copilot has multiple offerings for organizations and an offering for individual developers. All the offerings include both code completion and chat assistance. The primary differences between the organization offerings and the individual offering are license management, policy management, and IP indemnity.
Organizations can choose between GitHub Copilot Business and GitHub Copilot Enterprise. GitHub Copilot Business primarily features GitHub Copilot in the coding environment - that is the IDE, CLI and GitHub Mobile. GitHub Copilot Enterprise includes everything in GitHub Copilot Business. It also adds an additional layer of customization for organizations and integrates into GitHub.com as a chat interface to allow developers to converse with Copilot throughout the platform. GitHub Copilot Enterprise can index an organization’s codebase for a deeper understanding of the customer’s knowledge for more tailored suggestions and will offer customers access to fine-tuned custom, private models for code completion.
GitHub Copilot Individual is designed for individual developers, freelancers, students, educators, and open source maintainers. The plan includes all the features of GitHub Copilot Business except organizational license management, policy management, and IP indemnity.
What languages, IDEs, and platforms does GitHub Copilot support?
GitHub Copilot is trained on all languages that appear in public repositories. For each language, the quality of suggestions you receive may depend on the volume and diversity of training data for that language. For example, JavaScript is well-represented in public repositories and is one of GitHub Copilot’s best supported languages. Languages with less representation in public repositories may produce fewer or less robust suggestions.
GitHub Copilot is available as an extension in Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, Vim, Neovim, the JetBrains suite of IDEs, and Azure Data Studio. Although code completion functionality is available across all these extensions, chat functionality is currently available only in Visual Studio Code, JetBrains and Visual Studio. GitHub Copilot is also supported in terminals through GitHub CLI. With the GitHub Copilot Enterprise plan, GitHub Copilot is natively integrated into GitHub.com. All plans are supported in GitHub Copilot in GitHub Mobile. GitHub Mobile for Copilot Individual and Copilot Business have access to Bing and public repository code search. Copilot Enterprise in GitHub Mobile gives you additional access to your organization's knowledge.
What data has GitHub Copilot been trained on?
GitHub Copilot is powered by generative AI models developed by GitHub, OpenAI, and Microsoft. It has been trained on natural language text and source code from publicly available sources, including code in public repositories on GitHub.
Does GitHub Copilot “copy/paste”?
No, GitHub Copilot generates suggestions using probabilistic determination.
When thinking about intellectual property and open source issues, it is critical to understand how GitHub Copilot really works. The AI models that create Copilot’s suggestions may be trained on public code, but do not contain any code. When they generate a suggestion, they are not “copying and pasting” from any codebase.
To generate a code suggestion, the Copilot extension begins by examining the code in your editor—focusing on the lines just before and after your cursor, but also information including other files open in your editor and the URLs of repositories or file paths to identify relevant context. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
To generate a suggestion for chat in the code editor, the Copilot extension creates a contextual prompt by combining your prompt with additional context including the code file open in your active document, your code selection, and general workspace information, such as frameworks, languages, and dependencies. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
To generate a suggestion for chat on GitHub.com, such as providing an answer to a question from your chat prompt, Copilot creates a contextual prompt by combining your prompt with additional context including previous prompts, the open pages on GitHub.com as well as retrieved context from your codebase or Bing search. That information is sent to Copilot’s model, to make a probabilistic determination of what is likely to come next and generate suggestions.
Privacy
What personal data does GitHub Copilot process?
GitHub Copilot processes personal data based on how Copilot is accessed and used: whether via GitHub.com, mobile app, extensions, or one of various IDE extensions, or through features like suggestions for the command line interface (CLI), IDE code completions, or personalized chat on GitHub.com. The types of personal data processed may include:
User Engagement Data: This includes pseudonymous identifiers captured on user interactions with Copilot, such as accepted or dismissed completions, error messages, system logs, and product usage metrics.
Prompts: These are inputs for chat or code, along with context, sent to Copilot's AI to generate suggestions.
Suggestions: These are the AI-generated code lines or chat responses provided to users based on their prompts.
Feedback Data: This comprises real-time user feedback, including reactions (e.g., thumbs up/down) and optional comments, along with feedback from support tickets.
Does GitHub use Copilot Business or Enterprise data to train GitHub’s model?
No. GitHub does not use either Copilot Business or Enterprise data to train its models.
How does GitHub use the Copilot data?
How GitHub uses Copilot data depends on how the user accesses Copilot and for what purpose. Users can access GitHub Copilot through the web, extensions, mobile apps, computer terminal, and various IDEs (Integrated Development Environments). GitHub generally uses personal data to:
Deliver, maintain, and update the services as per the customer's configuration and usage, to ensure personalized experiences and recommendations
Troubleshoot, which involves preventing, detecting, resolving, and mitigating issues, including security incidents and product-related problems, by fixing software bugs and maintaining the online services' functionality and up-to-dateness
Enhance user productivity, reliability, effectiveness, quality, privacy, accessibility, and security by keeping the service current and operational
These practices are outlined in GitHub’s Data Protection Agreement (DPA), which details our data handling commitments to our data controller customers.
GitHub also uses certain personal data with customer authorization under the DPA, for the following purposes:
Billing and account management
To comply with and resolve legal obligations
For abuse detection, prevention, and protection, virus scanning, and scanning to detect violations of terms of service
To generate summary reports for calculating employee commissions and partner incentives
To produce aggregated reports for internal use and strategic planning, covering areas like forecasting, revenue analysis, capacity planning, and product strategy,
For details on GitHub's data processing activities as a controller, particularly for Copilot Individual customers, refer to the GitHub Privacy Statement.
How long does GitHub retain Copilot data for Business and Enterprise customers?
If and for how long GitHub’s retains Copilot data depends on how a Copilot user accesses Copilot and for what purpose. The default settings for Copilot Business and Enterprise Customers are as follows:
Access through IDE for Chat and Code Completions:
Prompts and Suggestions: Not retained
User Engagement Data: Kept for two years.
Feedback Data: Stored for as long as needed for its intended purpose.
All other GitHub Copilot access and use:
Prompts and Suggestions: Retained for 28 days.
User Engagement Data: Kept for two years.
Feedback Data: Stored for as long as needed for its intended purpose.
Why do some Copilot features retain prompts and suggestions?
Retaining prompts and suggestions is necessary for chat on github.com, mobile, and CLI Copilot because those features’ effectiveness depends on using thread history to improve responses. The Copilot model requires access to previous interactions to deliver accurate and relevant suggestions.
Does GitHub Copilot support compliance with the GDPR and other data protection laws?
Yes. GitHub and customers can enter a Data Protection Agreement that supports compliance with the GDPR and similar legislation.
Does GitHub Copilot ever output personal data?
While we've designed GitHub Copilot with privacy in mind, the expansive definition of personal data under legislation like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) means we can't guarantee it will never output such data. The Large Language Model (LLM) powering GitHub Copilot was trained on public code and there were instances in our tests where the tool made suggestions resembling personal data. These suggestions were typically synthesized and not tied to real individuals.
How does Copilot allow users to access, alter or delete personal data?
These actions are available to Copilot users as described in the GitHub Privacy Statement.
Responsible AI
What are the intellectual property considerations when using GitHub Copilot?
The primary IP considerations for GitHub Copilot relate to copyright. The model that powers Copilot is trained on a broad collection of publicly accessible code, which may include copyrighted code, and Copilot’s suggestions (in rare instances) may resemble the code its model was trained on. Here’s some basic information you should know about these considerations:
Copyright law permits the use of copyrighted works to train AI models: Countries around the world have provisions in their copyright laws that enable machines to learn, understand, extract patterns, and facts from copyrighted materials, including software code. For example, the European Union, Japan, and Singapore, have express provisions permitting machine learning to develop AI models. Other countries including Canada, India, and the United States also permit such training under their fair use/fair dealing provisions. GitHub Copilot’s AI model was trained with the use of code from GitHub’s public repositories—which are publicly accessible and within the scope of permissible copyright use.
What about copyright risk in suggestions? In rare instances (less than 1% based on GitHub’s research), suggestions from GitHub may match examples of code used to train GitHub’s AI model. Again, Copilot does not “look up” or “copy and paste” code, but is instead using context from a user’s workspace to synthesize and generate a suggestion.
Our experience shows that matching suggestions are most likely to occur in two situations: (i) when there is little or no context in the code editor for Copilot’s model to synthesize, or (ii) when a matching suggestion represents a common approach or method. If a code suggestion matches existing code, there is risk that using that suggestion could trigger claims of copyright infringement, which would depend on the amount and nature of code used, and the context of how the code is used. In many ways, this is the same risk that arises when using any code that a developer does not originate, such as copying code from an online source, or reusing code from a library. That is why responsible organizations and developers recommend that users employ code scanning policies to identify and evaluate potential matching code.
In Copilot, you can opt whether to allow Copilot to suggest code completions that match publicly available code on GitHub.com. For more information, see "Configuring GitHub Copilot settings on GitHub.com". If you have allowed suggestions that match public code, GitHub Copilot can provide you with details about the matching code when you accept such suggestions. Matching code does not necessarily mean copyright infringement, so it is ultimately up to the user to determine whether to use the suggestion, and what and who to attribute (along with other license compliance) in appropriate circumstances.
Does GitHub Copilot include a filtering mechanism to mitigate risk?
Yes, GitHub Copilot does include an optional code referencing filter to detect and suppress certain suggestions that match public code on GitHub.
GitHub has created a duplication detection filter to detect and suppress suggestions that contain code segments over a certain length that match public code on GitHub. This filter can be enabled by the administrator for your enterprise and it can apply for all organizations within your enterprise, or the administrator can defer control to individual organizations.
With the filter enabled, Copilot checks code suggestions for matches or near-matches against public code on GitHub of 65 lexemes or more (on average,150 characters). If there is a match, the suggestion will not be shown to the user.
In addition to off-topic, harmful, and offensive output filters, GitHub Copilot also scans the outputs for vulnerable code.
Does GitHub Copilot include features to make it easier for users to identify potentially relevant open source licenses for matching suggestions?
Yes, GitHub Copilot is previewing a code referencing feature as an additional tool to assist users to find and review potentially relevant open source licenses. Code referencing is currently available in Visual Studio Code. This feature searches across public GitHub repositories for code that matches a Copilot suggestion. If there’s a match, users will find its information displayed in the Copilot console log, including where the match occurred, any applicable licenses, and a deep link to learn more. The deep link will take users to a navigable page on GitHub.com to browse examples of the code match and their repository licenses, and see how many repositories—including ones without licenses—that code appears in, as well as links to those repositories. Copilot users can review this information to determine whether the applicable suggestions are suitable for use, and whether additional measures may be necessary to use them.
Who owns the suggestions provided by GitHub Copilot?
We don’t determine whether a suggestion is capable of being owned, but we are clear that GitHub does not claim ownership of a suggestion. Whether a suggestion generated by an AI model can be owned depends on many factors (e.g. the intellectual property law in the relevant country, the length of the suggestion, the extent that suggestion is considered ‘functional’ instead of expressive, etc).
If a suggestion is capable of being owned, our terms are clear: GitHub does not claim ownership.
GitHub does not claim ownership of any suggestion. In certain cases, it is possible for Copilot to produce similar suggestions to different users. For example, two unrelated users both starting new files to code the quicksort algorithm in Java will likely get the same suggestion. The possibility of providing similar suggestions to multiple users is a common part of generative AI systems.
Can GitHub Copilot introduce insecure code in its suggestions?
Public code may contain insecure coding patterns, bugs, or references to outdated APIs or idioms. When GitHub Copilot synthesizes code suggestions based on this data, it can also synthesize code that contains these undesirable patterns. Copilot has filters in place that either block or notify users of insecure code patterns that are detected in Copilot suggestions. These filters target the most common vulnerable coding patterns, including hardcoded credentials, SQL injections, and path injections. Additionally, in recent years we’ve provided tools such as GitHub Advanced Security, GitHub Actions, Dependabot, and CodeQL to open source projects to help improve code quality. Of course, you should always use GitHub Copilot together with good testing and code review practices and security tools, as well as your own judgment.
Is GitHub Copilot intended to fully automate code generation and replace developers?
No. Copilot is a tool intended to make developers more efficient. It’s not intended to replace developers, who should continue to apply the same sorts of safeguards and diligence they would apply with regard to any third-party code of unknown origin.
The product is called “Copilot” not “Autopilot” and it’s not intended to generate code without oversight. You should use exactly the same sorts of safeguards and diligence with Copilot’s suggestions as you would use with any third-party code.
Identifying best practices for use of third party code is beyond the scope of this section. That said, whatever practices your organization currently uses – rigorous functionality testing, code scanning, security testing, etc. – you should continue these policies with Copilot’s suggestions. Moreover, you should make sure your code editor or editor does not automatically compile or run generated code before you review it.
Can GitHub Copilot users simply use suggestions without concern?
Not necessarily. GitHub Copilot users should align their use of Copilot with their respective risk tolerances.
As noted above, GitHub Copilot is not intended to replace developers, or their individual skill and judgment, and is not intended to fully automate the process of code development. The same risks that apply to the use of any third-party code apply to the use of Copilot’s suggestions.
Depending on your particular use case, you should consider implementing the protections discussed above. It is your responsibility to assess what is appropriate for the situation and implement appropriate safeguards.
You’re entitled to IP indemnification from GitHub for the unmodified suggestions when Copilot’s filtering is enabled. If you do elect to enable this feature, the copyright responsibility is ours, not our customers. As part of our ongoing commitment to responsible AI, GitHub and Microsoft extends our IP indemnity and protection support to our customers who are empowering their teams with GitHub Copilot. See Microsoft's Copilot Copyright Commitment for more details.
Does GitHub Copilot support accessibility features?
We are conducting internal testing of GitHub Copilot’s ease of use by developers with disabilities and working to ensure that GitHub Copilot is accessible to all developers. Please feel free to share your feedback on GitHub Copilot accessibility in our feedback forum.
Does GitHub Copilot produce offensive outputs?
GitHub Copilot includes filters to block offensive language in the prompts and to avoid synthesizing suggestions in sensitive contexts. We continue to work on improving the filter system to more intelligently detect and remove offensive outputs. If you see offensive outputs, please report them directly to copilot-safety@github.com so that we can improve our safeguards. GitHub takes this challenge very seriously and we are committed to addressing it.
Will GitHub Copilot work as well using languages other than English?
Given public sources are predominantly in English, GitHub Copilot will likely work less well in scenarios where natural language prompts provided by the developer are not in English and/or are grammatically incorrect. Therefore, non-English speakers might experience a lower quality of service.
- Authentication with SAML single sign-on (SSO) available for organizations using GitHub Enterprise Cloud.