Today we would like to talk to you on a topic most interesting – JavaScript image manipulation libraries. And, to be more precise – those JavaScript image manipulation libraries that definitely deserve your particular attention when you develop your next spectacular web app. But, let’s not get ahead of ourselves and firstly answer the question “What is an Image Manipulation Library?”
What is an Image Manipulation Library
Let’s start with a simple description. An image manipulation library or IML is a tool that’s main goal is to help you systemize, organize and manipulate graphic elements of your app in different ways. Different image manipulation libraries typically serve different purposes and can perform such goals as cropping the images, resizing them, converting them from one format to another, improving their quality and many-many more. So, all and all, a tool to use when making a web app. Unless, of course, you want to make a dull monochrome app that contains no images whatsoever, which is an unrealistic scenario in a modern world, where design can make or break an app just as easily as its functionality or usability. Keep in mind that before adding images to your app, you need to make sure they all look great. You can make corrections yourself or delegate the task to a reliable image manipulation service
What does JavaScript Image Manipulation Libraries bring to the table?
The next question to discuss when is the reasoning for choosing an image manipulation library, based on JavaScript, for your next web app instead of, for example, C++-based ones. The answer is simple: even though at first glance JavaScript IMLs are metaphorically heavier, they are reliable and can create some simply astounding result.
The practical usage of some of the entries you are going to see in this article in a short time is a thing of beauty and will do nothing less than improve the development of your next web app by easing the work with the images. So, without any further delays, let’s get down to the list.
| Name | Features | Pitfalls | Pricing | GitHub Stars |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pica | Resizes large images in-browser, auto-selects best technology, reuses images for thumbnails. | – | Free |  |
| Lena.js | Simple editor with 22 filters, small size, allows custom filters. | Might be too basic for complex tasks. | Free | |
| Jimp | Zero native dependencies, universal, blitting, blurring, coloring, Node.js syntax. | May not be as powerful for advanced image manipulation. | Free |  |
| Grade | Generates complementary gradients based on 2 predominant colors, enhances aesthetics. | Limited to gradient generation, not a full-fledged image editor. | Free |  |
| MarvinJ | Numerous algorithms for color/appearance manipulation, automatic detection of corners and shapes. | Complexity might be overkill for simpler tasks. | Free |  |
| Compressor.js | Handles image compression via canvas.toBlob API, adjustable quality output. | Primarily focused on compression, less on editing features. | Free |  |
| Fabric.js | Creates and manipulates shapes, converts SVG to JavaScript, handles object attributes like colors, depth, etc. | May have a learning curve for more complex features. | Free | |
| CamanJS | Advanced techniques with an intuitive interface, customizable filters and plugins, regular updates. | Complexity and learning curve for advanced features. | Free |  |
| Cropper.js | Image cropping, scaling, rotating, zooming, aspect ratio setting. | Focused mainly on cropping, less on other editing aspects. | Free |  |
| Merge Images | Merges images onto a canvas, simplifies the process of transforming images to code. | Limited to merging images, not suitable for individual image editing. | Free |  |
| Blurify | Efficiently downgrades image quality, very lightweight (less than 2 kb). | Singular focus on blurring/downgrading quality. | Free |  |
| Doka | Variety of image editing options, rich UI, supports React, Vue, Svelte, Angular, jQuery. | More advanced than some may need, possibly overkill for simple tasks. | Paid |  |

JavaScript Image Manipulation Libraries
Pica
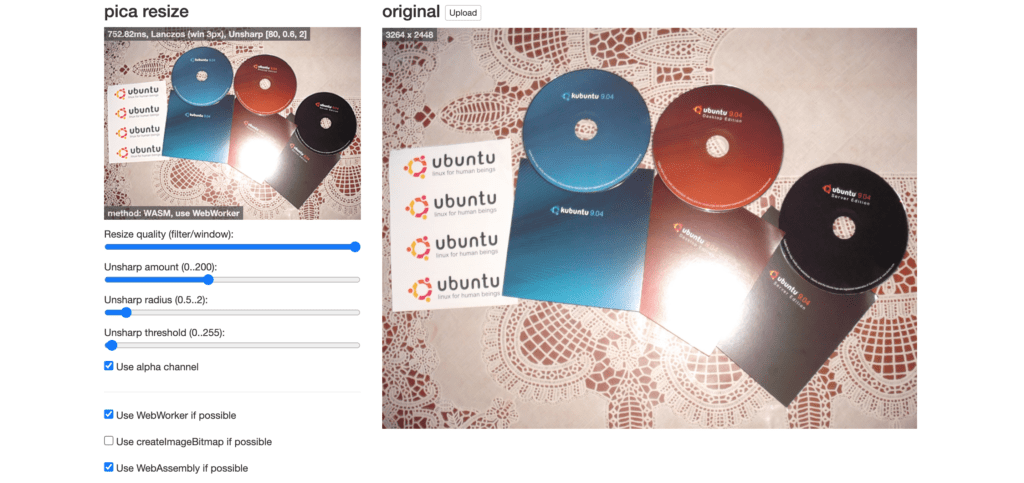
Pica is a prime tool for in-browser image resizing, most useful when you want to reduce an exceedingly large image into a suitable one in order to save upload time. It avoids the pixelation of an image and works at a suitably fast pace. It serves a great amount of server resources on image processing and can reuse your images into thumbnails in the browser. What’s also great about Pica is the fact that it auto selects such technologies as web workers, webassembly, createImageBitmap, pure JS, etc. automatically, so there is no need for you to do it yourself.
Lena.js

Lena.js can be described as a very simple, yet nice and neat image redactor and processor. It has a number (22 to be precise) image filters that you can play around with to improve your image. Lena.js is very small in size and has a killer feature that allows you to add your own filters, as it’s code is open to anyone at GitHub.
Jimp

Jimp stands for JavaScript image manipulation program and it does what it says on the tin a flawless fashion. Written for Node, this entirely JavaScript image processing library has zero native dependencies. It also has no external dependencies either, which makes it quite universal. Jimp can help you with such tasks as blitting, blurring, colouring, containing images and many others. What also advantages Jimp is its Node.js syntax that is will prove an easy use for people with Python or C++ primary prior experience.
Grade
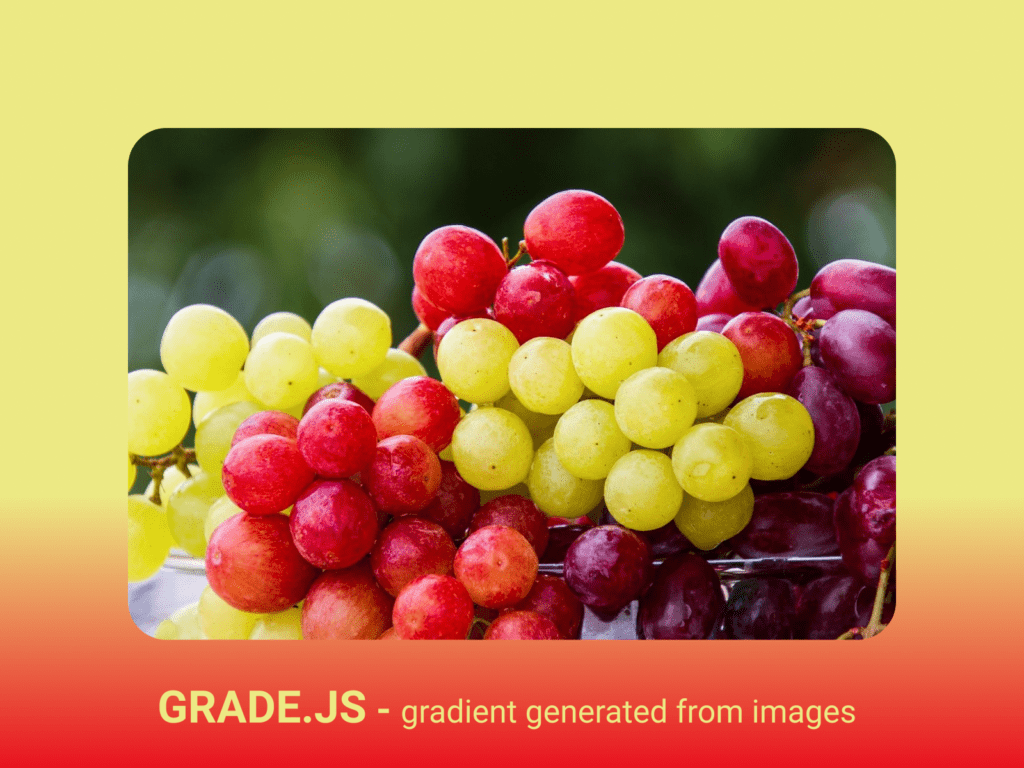
Grade (not a big surprise) is another JS library on our list. Its main selling point is producing complementary gradients that are automatically generated based on 2 colours that are determined predominant in the selected images. Such an effect allows your site or app to seem more seamless. Grade is an easy to use plugin that will add an aura of visually pleasing aesthetic to your finished product, which is always nice for both you and the end user.
MarvinJ

Now let’s get to a more intrinsically complex JavaScript image manipulation library. MarvinJ is a powerful Marvin Framework derivative that offers quite a number of algorithms for the images’ colour and appearance manipulation. It allows you to have an easier working process when it comes to such image processing fundamentals as corners and shapes, as MarvinJ is able to detect these features automatically. This way it simplifies the process of cropping out the image and even makes it more or less automated. And isn’t it, after all, the dream – to leave the tedious and boring thing like cropping the elements out to the machines while you can concentrate on more time-, imagination- and expertise-consuming tasks?
Compressor.js
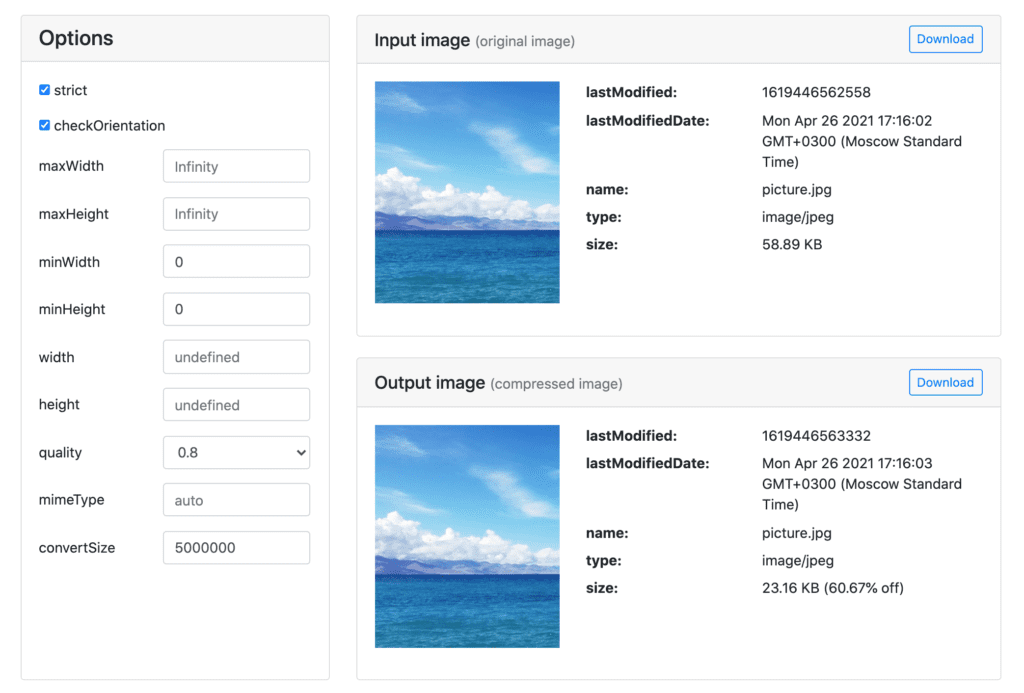
And now back to the simpler stuff. Compressor.js’s whole schtick is in the name – it handles the image compression and does it well. All thanks to the canvas.toBlob API that allows you to set the compression output quality of the image in the range from 0 to 1.
Fabric.js

Does your next web app need such simple, yet if used correctly, shapes as rectangles, circles, triangles and other polygons? May it be so that it requires more complex shapes? If the answer is “Yes” to any or both of the questions then Fabric.js is your guy – it will not only create all these shapes for you, but also allow you to manipulate every aspect of it, such as sizes, positions and rotations of the objects. But wait, there is more: control all the attributes of the upper-mentioned objects: colours, level of transparency. level of depth position and so on.
You might have noticed that we haven’t said a thing about images. But that meal is also on the menu, as Fabric.js allows to convert SVG images into JavaScript data and insert it into the canvas of the project. So, that’s killing two birds with one stone: cool shapes and SVG images in your apps code.
CamanJS

And, once again, to the more complex JavaScript image manipulation libraries. CamanJS is a combination of fantastic and sometimes quite advanced techniques and an intuitive interface. You can use presets and filters or tinker around toggling them yourself. The cherry on top is the ability to add your own filters and plugins, as well as constant updating, that bring new features and functions.
Cropper.js
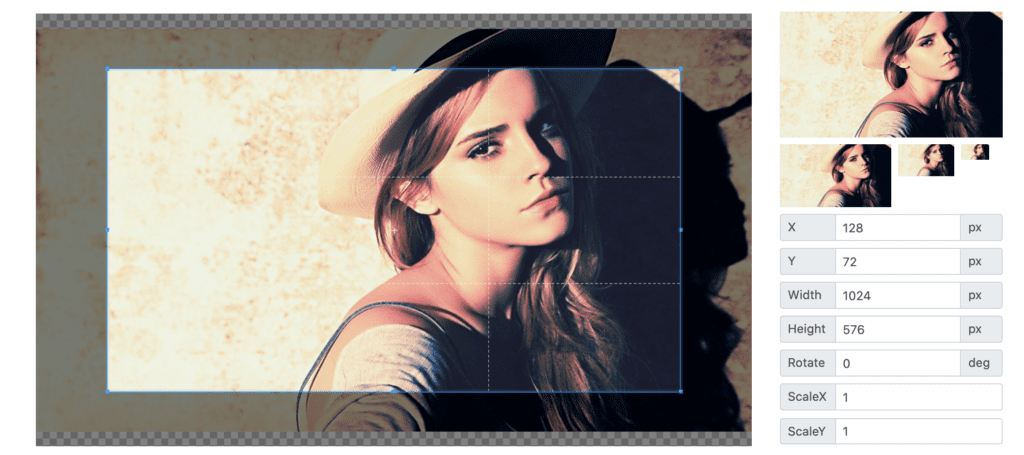
We duly hope that you are not tired of the “simple-complex” swings of our list, as here comes another simpler JavaScript image manipulation library. It allows you to crop the needed images, as well as scaling, rotating and zooming around the image. But the nicest thing about this JSIML is the ability to set the aspect ratio on the picture and crop accordingly.
Merge Images

A unique entree of this list, as Merge Images doesn’t crop, skew, or rotate the images. We hope, you’ve already guessed what this one does – it merges the given images onto one canvas, ridding you of the need to transform them into code and working on a canvas (pun intended).
Blurify
This JavaScript image manipulation library is tiny, as it weighs less than 2 kb. But it’s effectiveness doesn’t allow us to not include it on the list, as it downgrades the pictures that you provide it with, and does it gracefully.
Doka
Doka is a JIML which will provide you with a variety of image editing. It has a rich UI that warms your soul if needed. The support for React, Vue, Svelte, Angular, jQuery is also a nice and needed touch during the working upon the images. You will get around and understand this Library quite quickly.
Conclusions to have
And that’s the list. Conclusions to have are quite simple: your next project will benefit from using these JavaScript image manipulation libraries, as it will get you free from performing mundane tasks and you will find yourself in love with them in no time.
Start with one, if you feel cautious, add more if you feel adventurous, as it may actually require some tinkering to work the way you want it to work.
That’s it for today. Thanks for reading this article and stay tuned for our new ones!
Bonus! Creating Applications with Flatlogic Platform
We’ve covered JavaScript libraries for image manipulation. Now let us take a look at a quicker and easier way to create Applications. Sometimes an application must have specific features or peculiarities we have to craft by hand. Still, the bulk of all Apps work similarly and can be built from the same blocks. We created the Flatlogic Platform to do just that. It requires no special expertise, only a few choices. Let’s see what they are!
#1: Name the Project
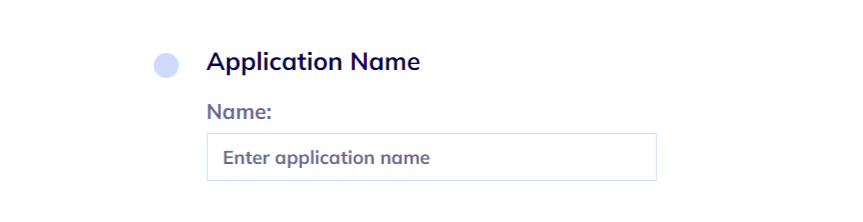
This step is rather straightforward. Name your project so it’s easier to find and recognize.
#2: Define Tech Stack
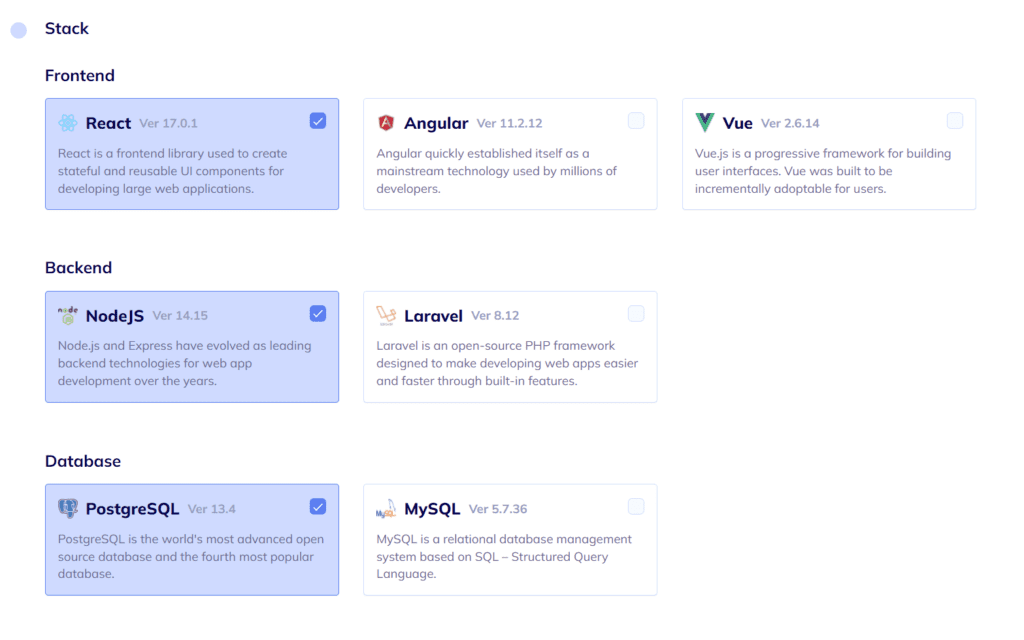
Next, we’ll choose the technologies our App’s components will run on. In the example above we’ve chosen React, NodeJS, and PostgreSQL for front-end, backend, and database, respectively.
#3: Choose the Design
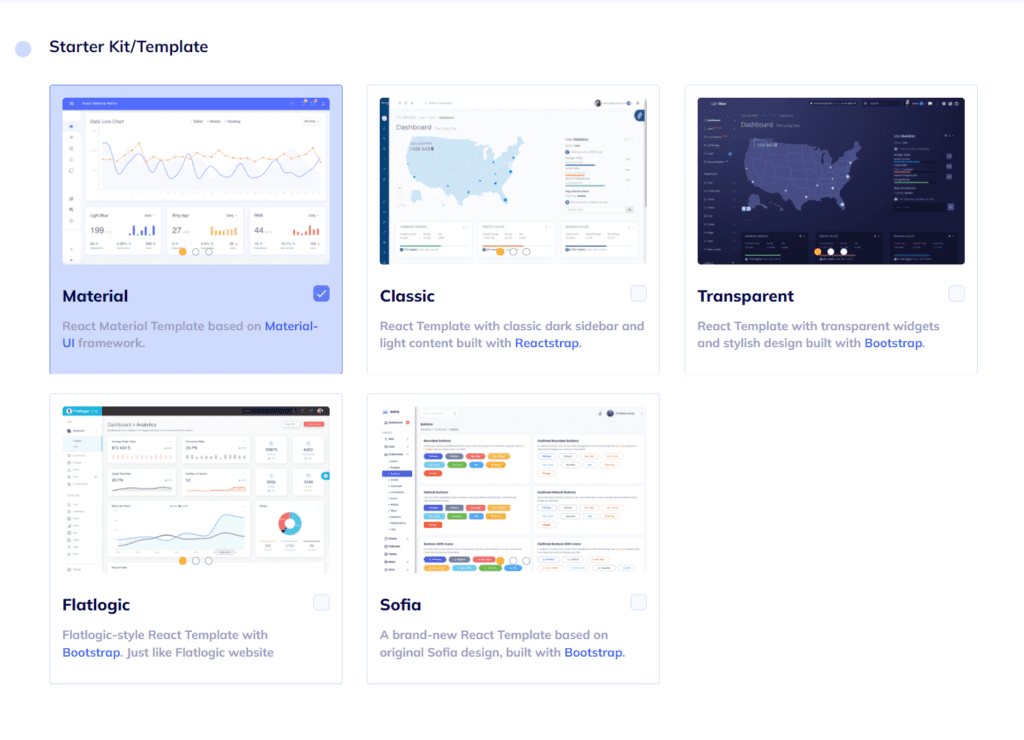
Choose the design type that appeals to you the most. You might spend a lot of time with this interface, so choose carefully!
#4: Create Database Schema
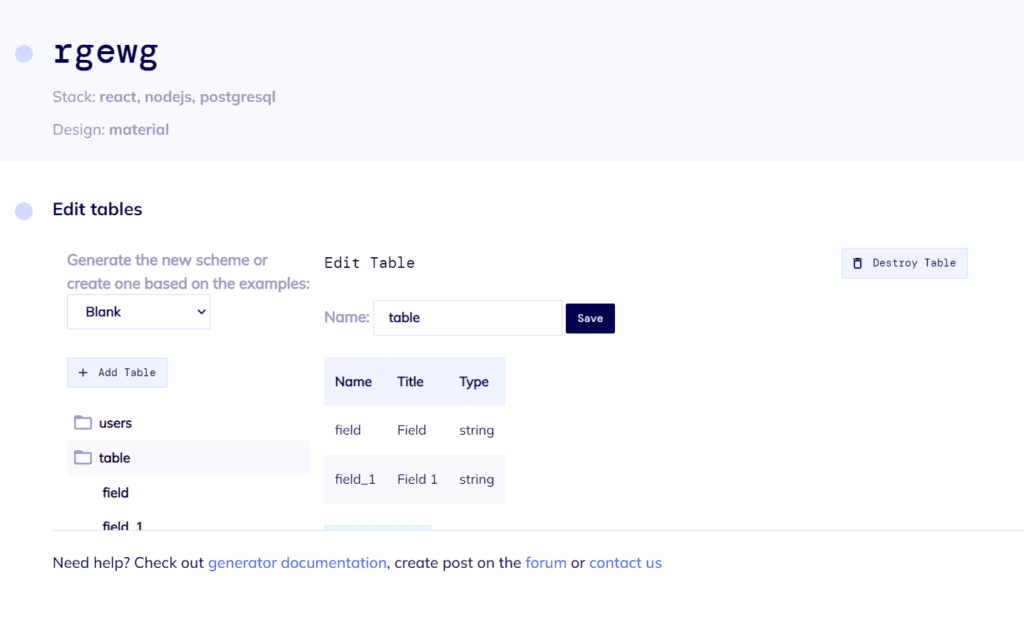
The integrated schema editor is rather easy to master. It lets you define fields, columns, and data types for the database. If you’re short on time, just pick one of the ready schemas.
#5: Finish the App
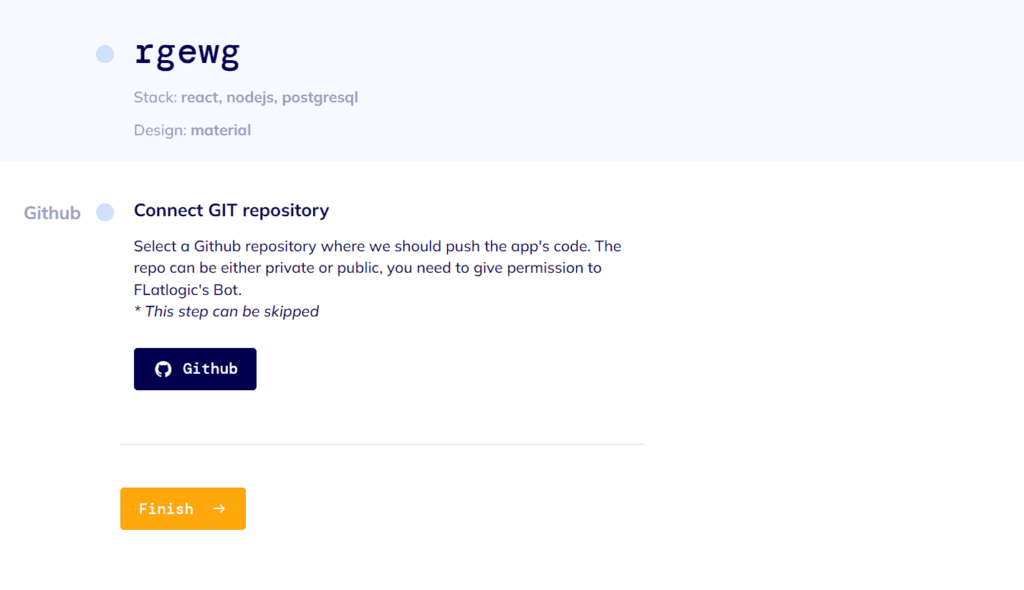
It’s time to review your choices and click “Finish”. Check the “Connect GIT repository” box if you want to. After a brief compilation, your App will be yours to deploy and use. Great job, sir or madam!


